Everything you need to know about cogeneration: The Ultimate Guide to Efficiency

In a global economy where energy costs define competitive advantages and the pressure to minimize greenhouse gas emissions is reshaping industries, traditional power generation models are failing.
The conventional method of purchasing electricity from the grid while separately burning fuel in a boiler for heat is inefficient and outdated. The answer to this challenge and the backbone of modern energy systems is cogeneration.
Technology is our drive, efficiency is our focus. At PowerUP, we understand that a cogeneration plant is more than just a collection of machinery. It is a strategic asset. Whether you operate a biogas facility in agriculture, manage complex industrial processes, or act as an Independent Power Producer (IPP), understanding this technology is key to maximizing your Return on Investment (ROI).
This comprehensive guide serves as your central resource. We will dissect the technology, explore the financial and environmental benefits, and show you how high-quality maintenance and spare parts suitable for leading engine brands like MWM and Jenbacher ensure your long-term success.
What is Cogeneration? Defining the Standard
To understand the impact of this technology, we must first define the cogeneration meaning. Also widely referred to as Combined Heat and Power (CHP) or simply cogen, it describes the simultaneous production of electricity and useful thermal energy from a single fuel source.
Unlike conventional power stations where vast amounts of heat are released into the atmosphere as waste via cooling towers, a chp system captures this energy. It repurposes the heat for district heating, generating steam for manufacturing, or providing hot water for facilities.
The difference in energy efficiency is staggering. A standard coal or gas power plant often operates at an efficiency of only 35% to 40%. The rest is lost. By contrast, a well-designed cogeneration plant located on-site eliminates transmission losses and utilizes the thermal output, achieving an overall efficiency of up to 90%.
This means you generate the same amount of energy using significantly less primary energy, directly reducing your environmental impact.
For a deeper explanation of the terminology and the distinction from separate generation, read our article:
The Technical Heart: How does a Cogeneration System work?
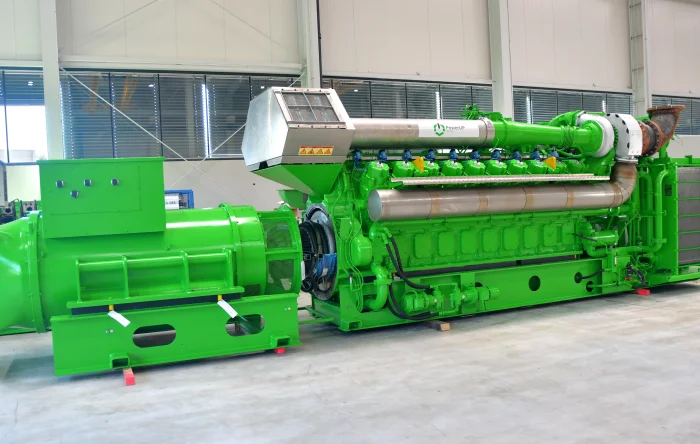
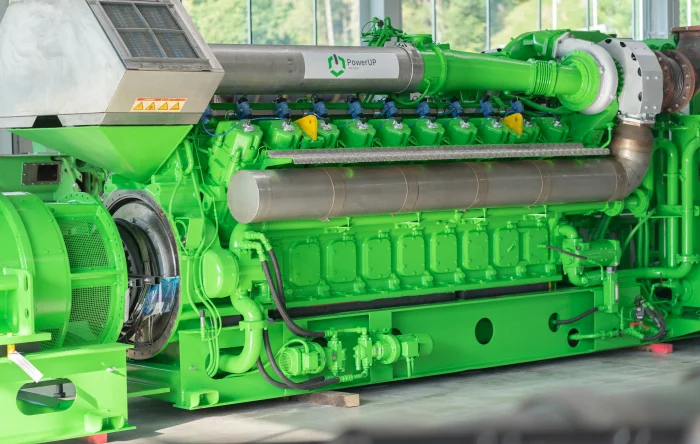
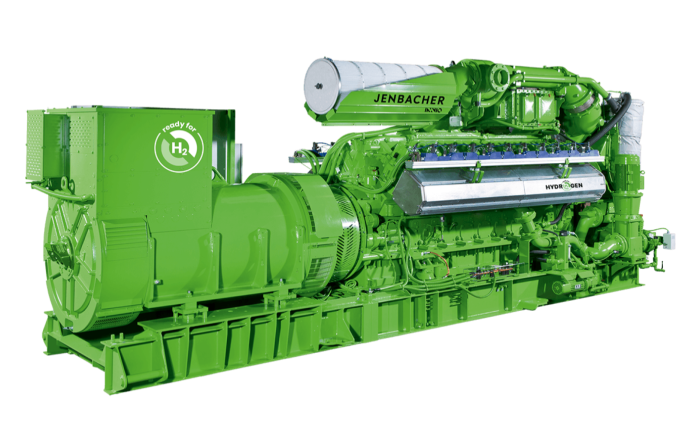
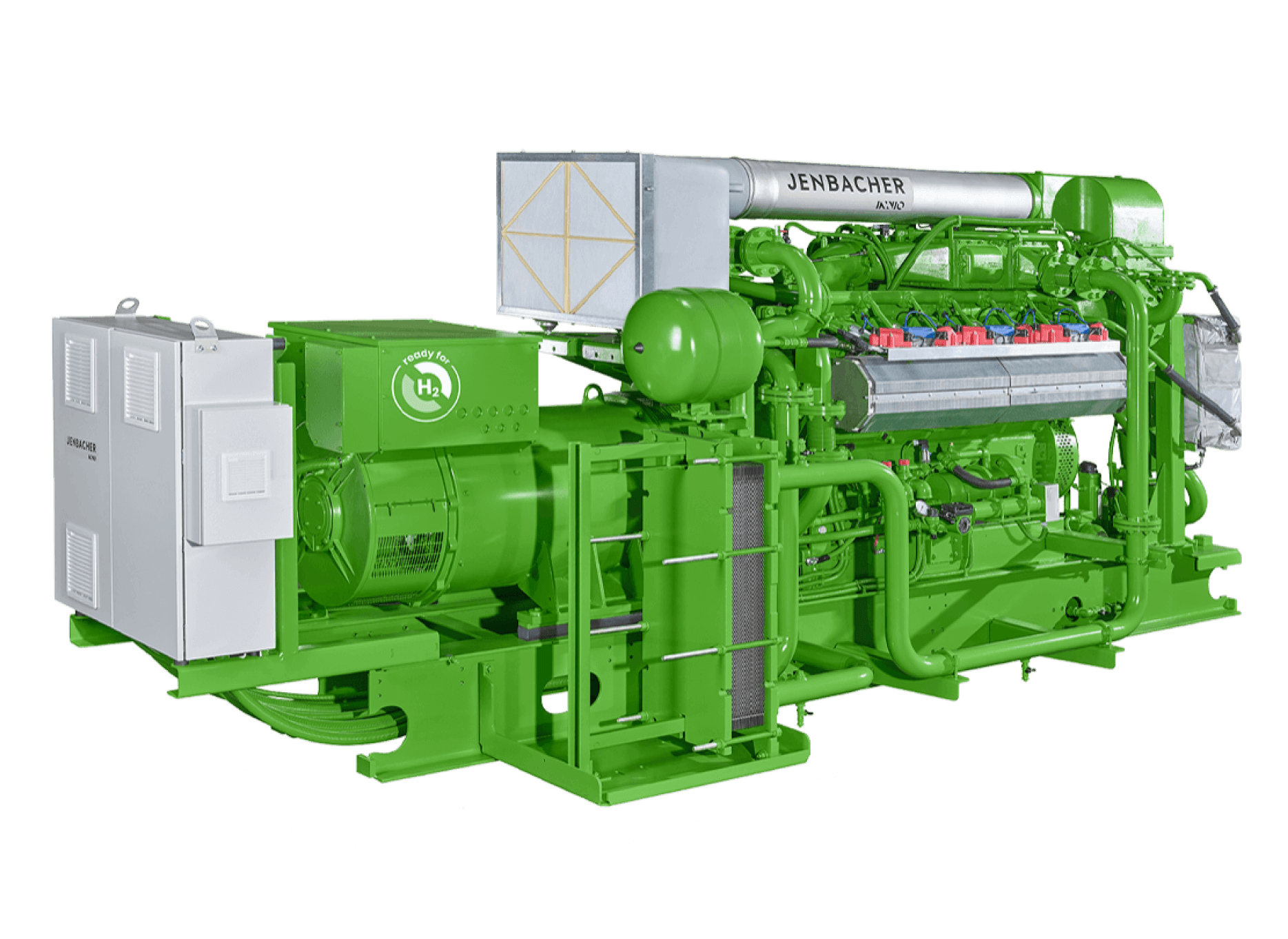
The mechanics behind cogeneration systems rely on converting the chemical energy of a fuel into mechanical work and heat. While there are various configurations involving gas turbines or steam turbines, the most common setup for distributed generation (ranging from 50 kW to 10 MW) is based on internal combustion engines, specifically reciprocating gas engines.
The Process Flow
The operation can be broken down into three integrated stages:
- The Prime Mover: A high-performance engine burns fuel (e.g., natural gas or biogas) to create mechanical force. This is the core component where PowerUP’s expertise in spare parts and upgrades comes into play.
- Electricity Generation: The engine drives an alternator (generator) to produce electric power. This electrical energy is either consumed by the end-user to offset grid purchases or fed into the public grid for revenue.
- Heat Recovery: This is the defining feature of chp. A system of heat exchangers captures thermal energy from the engine’s jacket water, oil cooler, and the hot exhaust gases. This recovered heat is transferred to a steam generator or hot water loop for immediate use.
For a detailed technical deep dive into components like the heat exchangerand control strategies, visit:
Fuel Flexibility: From Natural Gas to Renewables
Cogeneration is technology-neutral regarding the fuel and can utilize a wide range of energy sources. This flexibility makes it a resilient choice in the face of the ongoing energy transition.
Natural Gas as a Bridge Currently, natural gas is the dominant fuel for many cogeneration plants. It burns cleaner than coal and oil, producing significantly lower carbon emissions and pollutants like sulfur dioxide. For industries requiring high-temperature process heat, natural gas CHP remains the most cost-effective and reliable bridge technology to a low-carbon future.
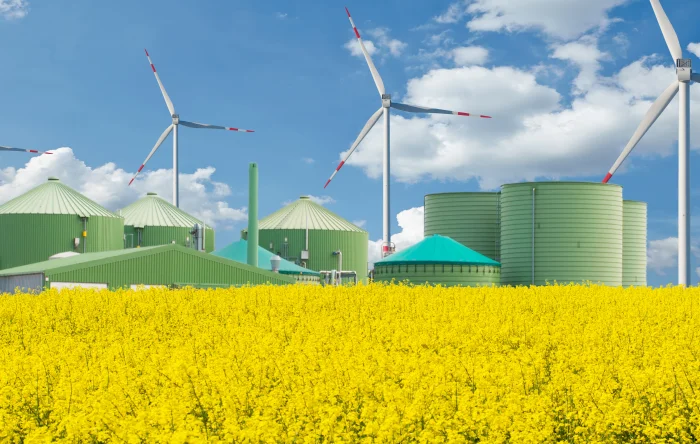
The Shift to Renewable Energy However, the true potential for sustainability lies in renewable sources. Engines are increasingly fueled by biogas, derived from agricultural waste, or solid waste in biomass plants.
When running on these fuels, the production of electricity becomes carbon-neutral. Furthermore, the industry is rapidly moving towards hydrogen. Modern engines are being designed or retrofitted to run on hydrogen blends, paving the way for zero-emission power generation independent of fossil fuels.
Learn more about the ecological classification and future fuels in our fact check:
The Economic and Ecological Case: Benefits of CHP
Why are governments globally, from the European Commission to the US EPA, promoting this technology? The answer lies in the massive advantages it offers to operators and the environment.
Financial Performance
The most immediate impact is on the bottom line. By generating power on-site, companies drastically reduce their energy costs and realize significant energy savings. They avoid peak demand charges and transmission fees associated with the grid.
Additionally, the high efficiency means less fuel is purchased for the same output. In many jurisdictions, feeding excess power back into the grid generates an additional revenue stream.
Environmental Sustainability
Cogeneration is a powerful tool for decarbonization. By burning less fuel through heat recovery, greenhouse gas emissions are slashed. For companies with strict ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) targets, installing a CHP unit is often the fastest way to reduce their carbon footprint.
Reliability and Resilience
Power systems are becoming increasingly volatile due to extreme weather and grid instability. A CHP system capable of “island mode” ensures that your industrial processes or data center continue to run during a blackout, providing invaluable business continuity.
However, owning a power plant also comes with challenges, such as high initial investment and maintenance requirements.
We analyze these pros and cons honestly in our dedicated article:
Applications: Where is CHP used?
The versatility of cogeneration systems allows them to be deployed across a wide spectrum of sectors to optimize their production processes:
- Industrial Facilities: Chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing plants use the process heat for steam, drying, and sterilization, integrating the energy flow directly into their production processes.
- District Heating: Large-scale power plants supply heat to residential networks, replacing thousands of individual boilers.
- Greenhouses: These facilities use the heat for climate control and clean the exhaust gases to use the CO2 as fertilizer for plant growth.
- Data Centers: Through trigeneration (Combined Cooling, Heat, and Power – CCHP), waste heat is converted into cooling via absorption chillers, efficiently cooling the servers.
Securing Efficiency: The Role of Maintenance
A cogeneration plant is a long-term investment, often calculated over 15 to 20 years. However, the theoretical efficiency of 90% can only be maintained in practice if the prime mover—the gas engine—is kept in peak condition. Wear on valves, pistons, and cylinder heads leads to efficiency losses and increased fuel consumption.
This is where PowerUP becomes your strategic partner. We do not just sell parts, we sell performance.
- Premium Spare Parts: We offer a portfolio of high-end components suitable for MWM and Jenbacher engines. Our parts are engineered to withstand the rigors of continuous operation, often outlasting standard components.
- Condition-Based Overhaul: Instead of rigid maintenance schedules, we advocate for overhauls based on the actual condition of the engine. This approach minimizes downtime and saves maintenance costs.
- Upgrades & Retrofits: We help you navigate the energy transition by upgrading control systems or retrofitting engines to handle new fuel types like biogas or hydrogen blends.
Conclusion
Cogeneration is not merely a temporary trend or a niche solution; it is the strategic cornerstone of a future-proof, resilient, and profitable energy supply. As we move towards a decentralized and decarbonized energy future, the ability to generate power and heat on-site with maximum efficiency becomes a decisive competitive advantage.
By integrating the production of electricity with intelligent heat recovery, chp systems solve the modern energy trilemma: ensuring security of supply, minimizing operational costs, and meeting strict environmental responsibilities.
Whether you are running on fossil fuels today or are already transitioning to biomass and hydrogen tomorrow, the principle of combined heat and power remains the most effective way to utilize primary energy.
However, the potential of a CHP plant is only fully realized through consistent high performance. A gas engine is a complex asset that requires expert care to prevent efficiency drift.
This is where the partnership with PowerUP makes the difference. By choosing spare parts suitable for MWM and Jenbacher engines and leveraging our condition-based overhaul strategies, you are not just maintaining a machine; you are optimizing an asset.
Do not let inefficiency eat into your profits or jeopardize your sustainability goals. Embrace the full potential of combined heat and power and prepare your operations for the era of renewable fuels. PowerUP is ready to guide you every step of the way—from the first spare part to a complete engine overhaul.