Natural gas – everything you need to know

Natural gas, a fundamental component of our energy supply, has a daily impact on the lives of many people. It serves not only as an energy source for heating and electricity generation, but also plays a crucial role in global trade and geopolitical discussions.
In this article, you will find all the essential information about natural gas and its significance in the modern world.
Introduction to Natural Gas
Natural gas is more than just a fuel, it is a central element in the global energy landscape. In the modern energy crisis, it represents a key resource that profoundly influences politics, the economy, and daily life. As a principal component of the gas supply for numerous nations, the natural gas market has undergone a dynamic evolution, encompassing geopolitical tensions as well as technological innovations.
The History of Natural Gas
The history of natural gas extends back to ancient times. While natural gas leaks were already known, the systematic utilization of natural gas did not begin until the 19th century. With the development of the natural gas market over the years, natural gas has emerged as one of the primary energy sources worldwide.
In recent decades, especially during the energy crisis and the opening of new markets, gas has significantly increased in importance. Today, it is not only a central component in the energy supply of many countries, but also a key player in the global energy market.
Do you want to know how natural gas is formed?
The significance of natural gas today
Due to the pros of natural gas, it has long since evolved into an indispensable energy source. Thanks to its versatility, it plays a central role in the gas supply for households, industries, and as a fuel for vehicles. Moreover, in the context of the energy crisis, natural gas has gained significance as a cleaner fossil fuel, contributing to the reduction of CO₂ emissions. The extraction and supply of natural gas are complex processes that require technical know-how and strategic planning. From drilling in deep deposits to distribution through international pipelines, the manner in which natural gas is extracted and transported.
Natural gas deposits
Natural gas deposits are geological formations located deep beneath the Earth’s surface where natural gas occurs naturally. These deposits can vary in terms of shape and depth, depending on the geological history of the specific region.
They are often found in connection with gas fields, which are specific regions where large amounts of natural gas are stored. The exploration and identification of natural gas deposits are crucial for the energy industry as they form the foundation for future natural gas extraction.
A big question is… How long can we continue to use natural gas?
Natural gas is considered a finite resource, and while current estimates suggest there are substantial reserves globally, the rate of extraction must be carefully managed to ensure sustainable use for future generations. That’s why there is a growing awareness of the need to diversify our energy mix to ensure long-term sustainability and mitigate environmental impacts.
Natural gas production
Natural gas extraction is a complex process that has continuously evolved over the decades. One of the primary methods used to extract natural gas is hydraulic fracturing, or fracking. This technique involves injecting water, sand, and chemicals into a wellbore at high pressure to fracture the rock and release the trapped gas.
However, natural gas is not just extracted from deep rock layers; it can also be found in significant quantities in gas fields and specific natural gas deposits. The technologies and methods employed vary depending on the geographic location and characteristics of the deposit, which presents a scientific and technical challenge for extraction.
Security of supply
Ensuring the security of natural gas supply is a crucial topic in energy policy and economy. It guarantees the uninterrupted flow and availability of natural gas for households, businesses, and industries.
The secure and uninterrupted supply of natural gas is of utmost importance in Europe, as many countries heavily rely on imports. Disruptions, whether caused by geopolitical tensions or technical issues, can have significant impacts on the energy market and the economy. Therefore, investments in infrastructure, gas storage, and diversifying sources of supply are crucial in order to maintain a stable and reliable gas supply.
The international natural gas market
The international natural gas market is a complex network that consists of producers, suppliers, and consumers, all of which are influenced by geopolitical, economic, and technological factors. In a globally interconnected world, where the demand and supply of energy are in constant flux, this market plays a crucial role in ensuring the global energy supply.
In the following, we will examine the main actors, dynamics, and challenges of this market in more detail and analyze their impact on Europe and the world.
The main actors
The international natural gas market is dominated by a number of key players that have a major influence on supply, demand, and pricing. Leading natural gas producers include countries such as Russia, Norway, the USA, and the Netherlands. In particular, Russia, often represented by its state-owned companies, is a primary supplier to many European countries. The Ukraine plays a critical role as a transit country for gas supply in Europe.
On the consumer side, Europe is at the forefront, with Germany, Italy, and France being among the largest importers. These countries, along with the operators of various multinational energy companies, play a significant role in shaping the dynamics and strategies in the global gas market.
Gas prices and trade
The prices of natural gas are influenced by numerous factors that impact both its supply and demand. These factors often include geopolitical tensions, supply agreements, storage capacities, and weather conditions. Trading of natural gas occurs in both regional and global markets, with Europe serving as a central hub.
Contracts can be long-term and price-indexed, based on oil price indices, or they can be based on spot market prices. The recent introduction of liquefied natural gas (LNG) has revolutionized the trade by enabling long-distance transport without the need for pipeline infrastructure, thereby introducing new market players and dynamics into the natural gas market.
Types and Qualities of Natural Gas
Natural gas is not all the same. It can vary in composition and quality depending on its origin and processing. These differences directly affect how it can be used, transported, and priced. In the following section, we will explore the various types of natural gas, such as LNG, methane, and biogas, and examine their specific characteristics and applications in more detail.

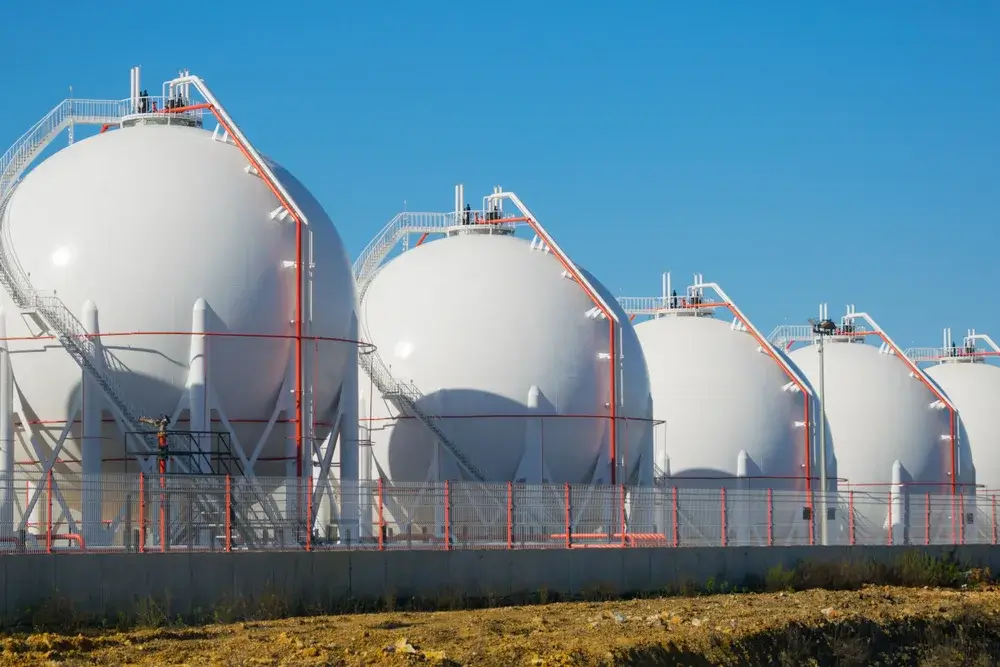
LNG and liquefied natural gas
LNG, short for Liquefied Natural Gas, refers to natural gas that has been cooled to extremely low temperatures and transformed into liquid form. This process greatly reduces the volume of the gas, facilitating its transportation over long distances, particularly by ship.
Liquefied natural gas, or LNG, is essentially another term for flüssigerdgas, both denoting the state in which natural gas is in its liquid form rather than gaseous. This technology has had a transformative impact on the global energy sector by enhancing international trade without the need for gas pipelines and improving the security of natural gas supply.
H-Gas, L-Gas, and biomethane
H-gas and L-gas are two distinct qualities of natural gas, with H-gas referring to high-calorific gas and L-gas referring to low-calorific gas. H-gas has a higher energy content and a higher methane content, whereas L-gas, often sourced from specific geographic regions, has a lower methane content.
On the other hand, biomethane is a renewable gas that is produced by fermenting organic materials such as agricultural waste. After undergoing treatment, it can be directly injected into the natural gas grid or used as an alternative fuel. Each of these types of gas has its specific applications and advantages in the energy market.

Gas Mixtures
Gas mixtures refer to combinations of different gases that are often found in natural gas deposits. While methane is the primary component of natural gas, other gases such as ethane, propane, and nitrogen may also be present in varying quantities. The exact composition of a gas mixture can vary depending on the source location of the natural gas.
These mixtures are typically processed in treatment facilities to eliminate unwanted components and enhance the quality of the gas. Understanding the composition and characteristics of gas mixtures is naturally essential for their efficient utilization and commercialization.
The utilization of natural gas
Natural gas has gained significant importance in recent decades and has emerged as one of the primary energy sources worldwide. Its versatility allows for a wide range of applications, ranging from power generation to its use as a fuel. Moreover, with the ongoing integration of renewable energy sources into the energy system, natural gas plays a crucial role in facilitating the transition towards sustainable energy.

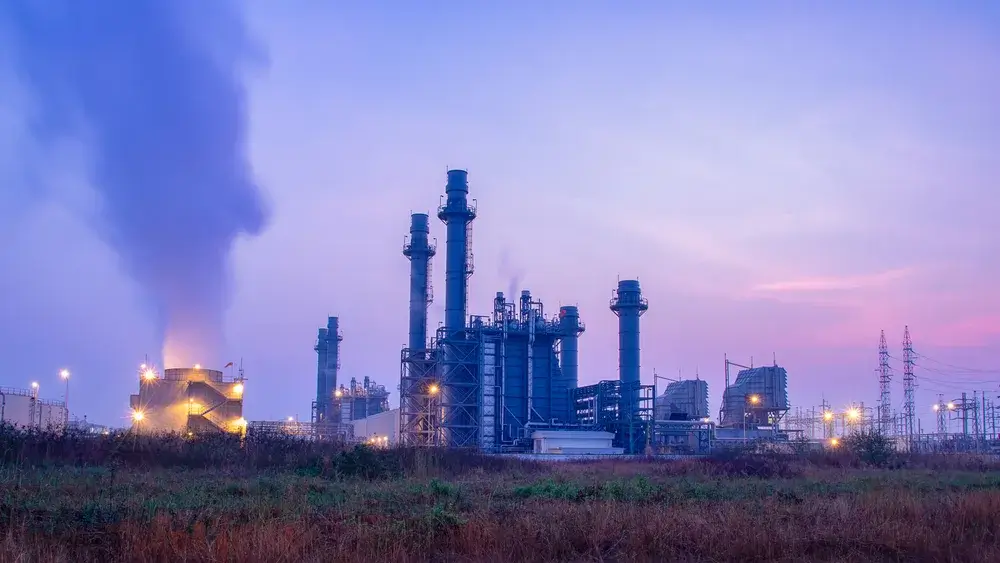
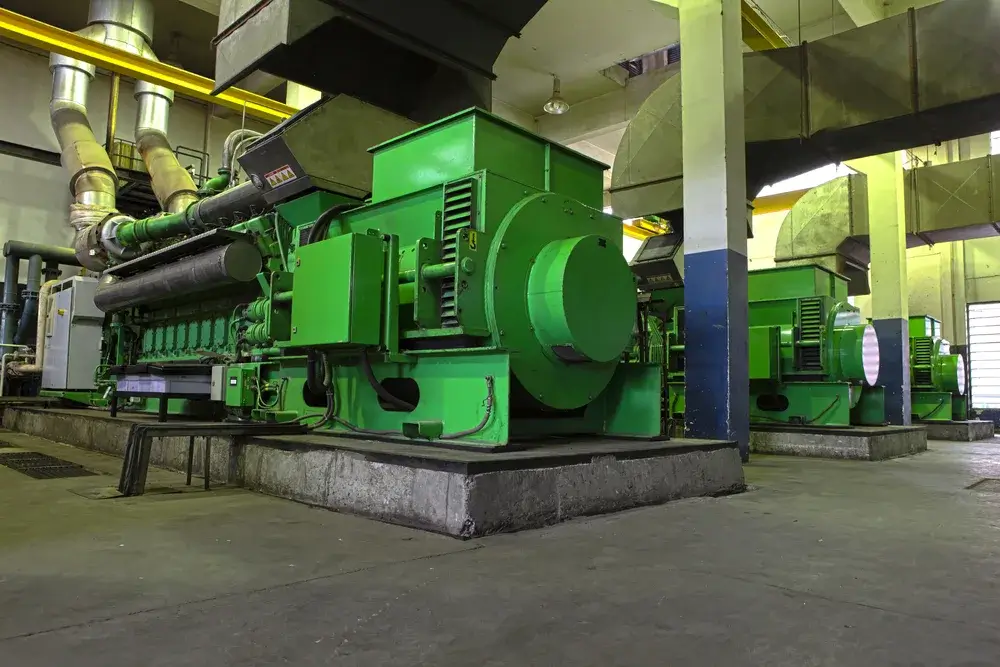
Natural gas in power generation
Natural gas has become one of the predominant energy sources for electricity generation. In comparison to other fossil fuels, it burns more cleanly and emits lower levels of CO₂, making it a preferred option for many modern power plants.
Due to its high efficiency and fast start-up capability, natural gas is extremely well-suited for peak-load power plants, which can be rapidly adjusted to compensate for fluctuations in the energy system.
When used as a fuel, natural gas has gained popularity in recent years as a more environmentally friendly alternative to conventional fossil fuels like gasoline and diesel. Natural gas vehicles (CNG vehicles) emit fewer harmful emissions and can contribute to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
Moreover, operating costs are often lower as natural gas is more cost-effective than gasoline or diesel in many regions. The expanding network of gas stations and the advancements in technology for natural gas vehicles have further amplified this trend and facilitated broader acceptance of natural gas as a fuel. Additionally, the integration of natural gas into renewable energy systems has gained significance due to the growing emphasis on climate protection and the urgency to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Natural gas can act as a transitional technology, easing the transition to a fully renewable energy system.
Due to its flexibility and rapid response time, natural gas can also serve as a backup when renewable sources such as wind or solar are insufficient. This ensures a consistent energy supply while the proportion of renewable energies in the grid increases. The combination of natural gas and renewable energies can therefore contribute to an efficient, reliable, and more sustainable energy system. Through constant advancements, gas engines naturally continue to improve and become more efficient.
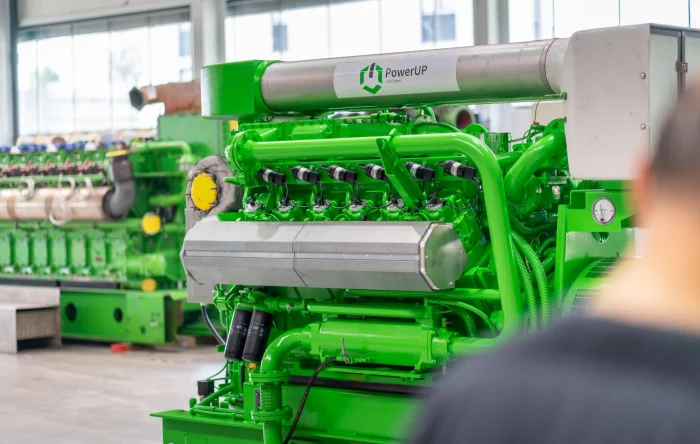
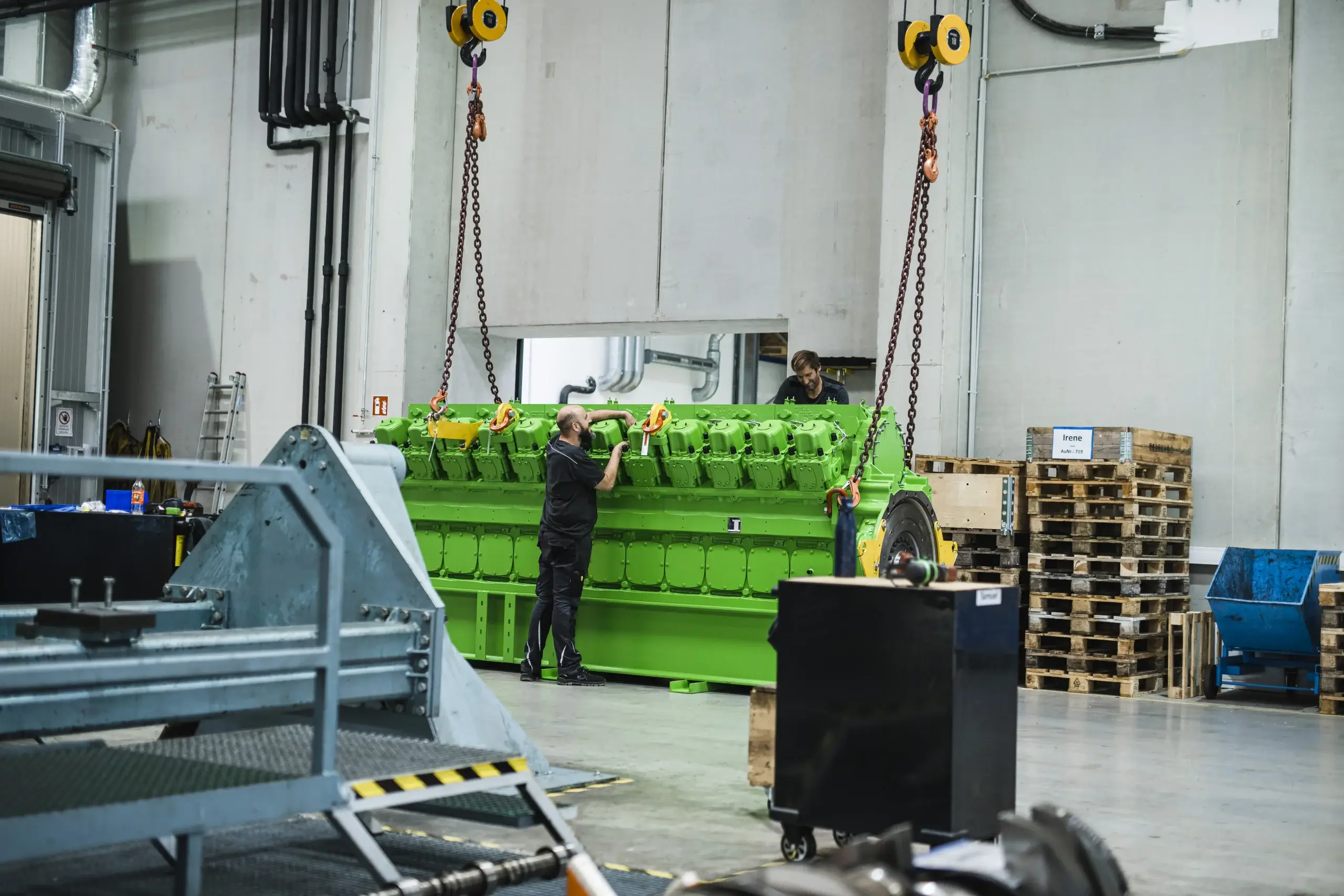
PowerUP – Your partner for gas engines
Continuous innovation is necessary in order to overcome challenges such as premature wear, reduction in engine performance, or high initial and maintenance costs.
With a variety of solutions for your gas engine, PowerUP is your go-to partner for the INNIO Jenbacher, MWM, and Caterpillar brands. From specially designed replacement parts to repairs, emergency engines, and container solutions – our expertise in this field ensures that our customers always receive the highest level of service.