Everything you need to know about Captive Power Plants
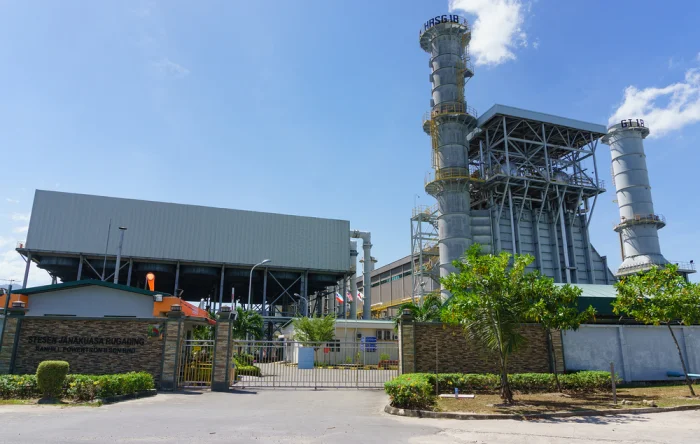
Captive Power Plants (CPPs) are specialized energy facilities designed for the exclusive use of the entity that owns or operates them, often industrial or commercial establishments, to ensure a reliable and cost-effective power supply. These plants are typically located on-site or near the premises of the user, allowing for greater control over energy production and consumption.
In this article, you will learn everything about Captive Power Generation in general, Captive Power Plants, the advantages and disadvantages, fuels that can be used and why CCPs are so popular.
What is a Captive Power Plant?
A Captive Power Plant (CPP) acts as a facility that is specifically constructed and operated by an industrial or commercial entity to generate electricity primarily for its own use.
Unlike conventional power plants that supply electricity to the general public through the national grid, CPPs serve the exclusive needs of the entity that owns them, providing a self-reliant source of energy. This setup allows businesses to mitigate the risks associated with power outages and fluctuations in electricity prices, ensuring a stable and cost-effective supply of power.
CPPs can vary in size and technology, ranging from fossil fuel-based generators to renewable energy sources like biogas or solar, tailored to meet the specific energy demands and sustainability goals of the entity.
How does a Captive Power Plant generate electric power?
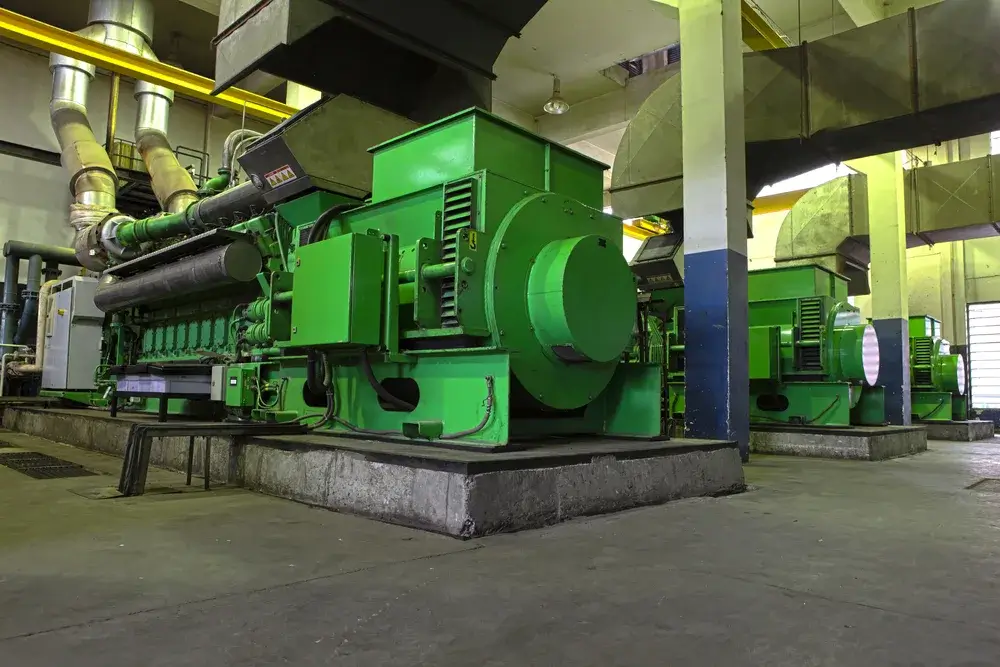
Captive Plants generate electricity off-grid by converting energy from various fuel sources through appropriate technologies. Fossil fuel-based CPPs burn fuel to produce steam, driving turbines connected to generators that convert mechanical energy into electricity.
Renewable energy CPPs, like solar or wind, use photovoltaic cells or turbines to directly convert sunlight or wind into electrical power. Biomass plants similarly burn organic materials for electricity generation.
The core of the process lies in the generator, which is crucial for transforming mechanical energy into electricity, tailored to meet the specific energy needs of the plant’s owner. This setup allows for a reliable and efficient electricity supply, often with a focus on minimizing environmental impact.
Managing Surplus Power in Captive Power Plants
Captive Power Plants (CPPs) with substantial generation capacity often produce surplus power, exceeding the energy requirements of the entity they serve. This excess generation capacity can be a strategic asset, offering opportunities beyond merely meeting internal demand.
Surplus power from CPPs can be directed in several ways, such as selling it to the national grid, supplying neighboring businesses under power purchase agreements, or storing it using battery storage technologies and power stations for later use. The generation and management of surplus power highlight the plant’s operational efficiency and the strategic advantage of having an in-house generation plant.
It allows businesses to not only secure a reliable and cost-efficient power supply, but also to potentially create an additional revenue stream or enhance energy security by maintaining a reserve of electricity.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a Captive Power Plant?
Captive Generation offers a mix of benefits and drawbacks for businesses considering their adoption. Here’s a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
- Reliability: Ensures a consistent and reliable power supply, reducing dependency on the national grid and mitigating the impact of power outages.
- Cost Savings: Potentially lowers energy costs in the long run, especially in regions with high electricity tariffs or unstable supply, by optimizing production based on the entity’s own operational schedules and energy consumption patterns.
- Energy Efficiency: Allows for improved energy efficiency through the optimization of power generation and usage, including the potential for waste heat recovery in industrial processes.
- Environmental Control: Provides the opportunity to incorporate cleaner and renewable energy sources, helping businesses reduce their carbon footprint and comply with environmental regulations.
Disadvantages
- High Initial Investment: Requires a significant upfront capital investment in plant construction, equipment, and technology.
- Operational and Maintenance Challenges: Demands specialized expertise for operation and maintenance, which can add to the operational costs and complexity.
- Regulatory and Compliance Issues: May involve navigating complex regulatory, environmental, and compliance requirements, depending on the location and the type of energy sources used.
- Resource Dependency: For plants relying on fossil fuels, there’s a risk of volatility in fuel prices and supply, which can affect the cost-effectiveness and sustainability of the power plant.
This balance between the pros and cons must be carefully considered by entities looking to establish a Captive Power Plant, ensuring it aligns with their operational needs, financial capacity, and long-term goals.
What is the difference between Cogeneration/CHP Plants and Captive Power Plants?
Cogeneration or Combined Heat and Power (CHP) plants and Captive Power Plants (CPPs) are both designed to meet specific energy needs, but they differ significantly in their approach and functionality.
Cogeneration or CHP plants are highly efficient systems that simultaneously generate electricity and useful thermal energy (such as steam or hot water) from the same energy source, typically utilized in industrial processes or for heating and cooling purposes. This dual output maximizes the energy yield from the fuel used, making CHP plants an energy-efficient choice.
On the other hand, Captive Power Plants are primarily focused on generating electricity for the exclusive use of the entity that owns them, with the primary goal of ensuring a reliable and cost-effective power supply.
While some CPPs may also utilize waste heat for industrial processes, their main function is to produce electricity, not the combined production of power and thermal energy characteristic of cogeneration plants. Thus, the key difference lies in the dual-purpose energy generation of CHP plants versus the electricity-centric focus of CPPs.
Which fuels can be used for Captive Power Plants?
Captive Power Plants (CPPs) are versatile in their fuel source options, allowing them to adapt to various energy needs and environmental considerations. The choice of fuel depends on factors such as availability, cost, efficiency, and the environmental impact. Common fuels used in CPPs include:
Fossil Fuels: Coal, natural gas, and diesel are widely used due to their high energy content and relatively easy availability. However, their environmental impact, including greenhouse gas emissions, often necessitates the implementation of pollution control technologies.
Renewable Energy Sources: The biogas industry, solar energy, wind and hydro power offer clean energy alternatives, helping businesses reduce their carbon footprint and comply with environmental regulations. These sources are particularly attractive for entities committed to sustainable energy practices.
Waste-to-Energy: Some industries generate significant amounts of waste that can be used as fuel in CPPs. This includes biomass waste, industrial by-products, or municipal solid waste, turning a disposal problem into an energy solution.
Hybrid Systems: Combining multiple fuel sources, such as solar and natural gas, can enhance reliability, reduce environmental impact, and optimize fuel usage based on availability and cost.
Why are Captive Power Plants so popular in India?
Captive Power Plants (CPPs) have gained significant popularity in India due to a combination of economic, operational, and infrastructural factors. India’s rapid industrial growth has led to an increased demand for reliable and cost-effective power supply, a need that CPPs are well-equipped to meet.
The country’s power infrastructure, while extensive, faces challenges such as frequent power outages, voltage fluctuations, and peak-time shortages, which can significantly disrupt industrial operations.
Furthermore, the high cost of electricity from the grid, coupled with the regulatory support for CPPs, makes them an attractive option for businesses seeking to control their energy costs and ensure uninterrupted production.
The availability of a wide range of fuels, including coal, natural gas, and renewable energy sources, also provides flexibility in setting up CPPs across different regions. Additionally, the Indian government’s focus on enhancing energy security and promoting sustainable energy practices has encouraged the adoption of CPPs, especially those utilizing renewable energy sources.
This confluence of factors has cemented the role of CPPs as a critical component of the energy strategy in India and Asia, particularly for industries requiring high-quality, reliable power to maintain competitive advantage.
PowerUP Services and Spare Parts for Captive Power Plants
PowerUP offers a comprehensive range of gas engine services and spare parts tailored for Captive Power Plants, ensuring their efficient and reliable operation. With expertise in gas engine repair, gas engine upgrades, and other services, PowerUP provides everything needed to keep your power plant running smoothly.
Our inventory of gas engine spare parts for MWM® and Jenbacher® guarantees optimal performance and longevity of your equipment, making PowerUP an essential partner for maintaining energy self-sufficiency.
FAQs for Captive Power Plants
What incentives are available for setting up Captive Power Plants (CPPs)?
Governments and regulatory bodies often offer a range of incentives for the establishment of Captive Power Plants. These can include tax benefits, subsidies for using renewable energy sources, and financial assistance for technology upgrades, aiming to encourage self-sufficiency and sustainability in energy generation.
How do Captive Power Plants integrate with grid-connected distribution systems?
Captive Power Plants can integrate with grid-connected distribution systems to sell surplus power back to the grid or exchange power during periods of low generation. This integration involves meeting regulatory standards and technical requirements to ensure safety, reliability, and compatibility with the grid infrastructure.
How can Captive Power Plants in Karnataka contribute to the state’s renewable energy goals?
Captive Power Plants (CPPs) in Karnataka have a unique opportunity to contribute significantly to the state’s renewable energy goals by incorporating renewable energy sources into their energy mix. By utilizing solar, wind, biomass, or hydro energy for power generation, CPPs can help Karnataka achieve its targets for renewable energy capacity, reduce carbon emissions, and promote sustainable industrial growth within the state. This alignment with renewable energy initiatives not only supports environmental objectives but also enhances energy security and reliability for businesses operating in Karnataka.
How does selling surplus power from Captive Power Plants benefit the energy ecosystem?
Selling surplus power from Captive Power Plants benefits the energy ecosystem by adding to the grid’s power supply, enhancing stability, and promoting the use of renewable energy. This practice can lead to more efficient use of resources, reduce dependency on fossil fuels, and support the transition to a more sustainable energy system.
What role do Captive Power Plants play in promoting renewable energy adoption?
Captive Power Plants play a crucial role in promoting renewable energy adoption by incorporating clean energy sources such as solar, wind, and biomass into their operations. This not only helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions but also aligns with global efforts towards sustainability and energy security, making CPPs integral to the transition towards a greener energy future.