How does combined heat and power (CHP) work? Technology in Detail
Every plant operator knows the sound of a running gas engine. It is the sound of productivity. But within this rhythmic hammering lies far more than just power generation. It is a complex interplay of thermodynamics, mechanics, and intelligent control that determines whether your operation is profitable at the end of the year or burning money through high energy bills.
Understanding how does combined heat and power work is the first step to mastering energy efficiency. Technology is our drive, efficiency is our focus. At PowerUP, we see daily that understanding the function of your own plant is the key to optimization.
In this article, we dive deep into the technology of CHP systems and explain how they turn fuel sources into profit.
The Basic Principle: Efficiency instead of Waste
To understand how does CHP work, we must first detach ourselves from the classic image of generating power. In conventional power plants (often relying on huge steam turbines), the electricity production process is surprisingly inefficient. Up to 60% of the primary energy contained in fossil fuels vanishes unused into the atmosphere as waste heat via cooling towers.
CHP technology (Combined Heat and Power) reverses this principle. It is based on the realization that heat is not a waste product, but useful thermal energy that is worth money. By capturing this heat on-site, a CHP unit achieves a higher efficiency—often exceeding 90%. This significantly lowers greenhouse gas emissions and energy costs.
Step-by-Step: How the CHP Process Works
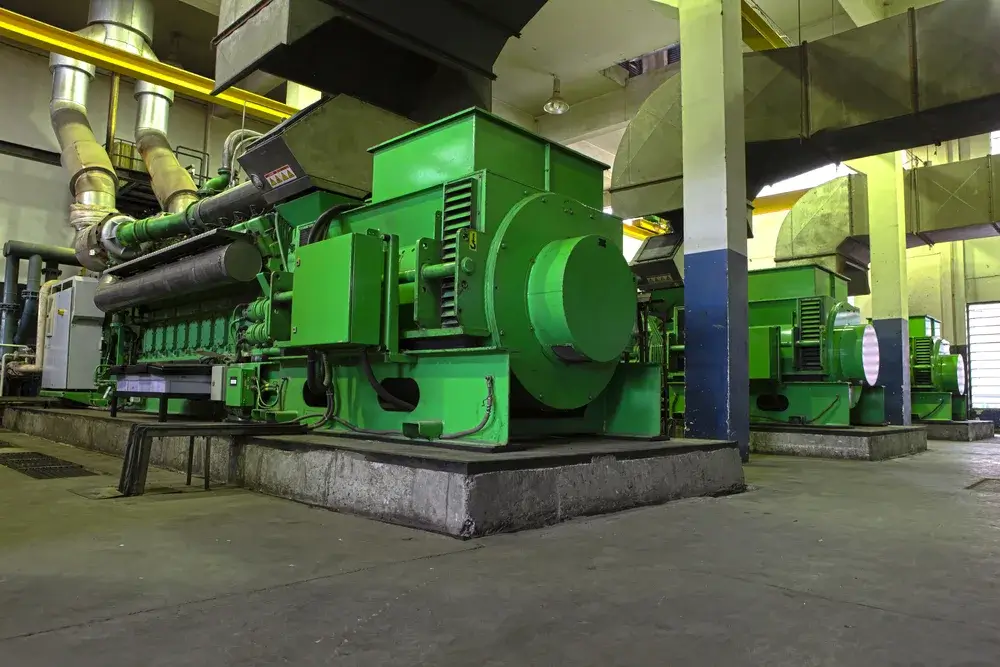
A cogeneration plant consists of four main components: The prime mover (engine), the generator, the heat recovery system, and the control system. Here is the process in detail:
1. The Prime Mover: Creating Mechanical Energy
Everything starts with the drive unit. In most distributed generation applications, such as industrial facilities, commercial buildings, or biogas plants, this is a reciprocating engine.
These are high-performance gas engines, for example, from MWM or Jenbacher. The engine burns a fuel—such as natural gas, biogas, landfill gas, or hydrogen blends. This combustion creates mechanical force.
2. The Generator: Electricity Generation
The engine shaft drives a generator. This converts the mechanical rotation into electric power. This power production happens directly at the point of use, which eliminates distribution losses associated with the public grid. The electricity flows into your facility’s power system or is fed into the grid.
3. Heat Recovery: Capturing Thermal Energy
This is the magic moment of cogeneration. An engine gets extremely hot during operation. A CHP system uses heat exchangers to capture this energy from two main sources:
- Engine Jacket & Oil: Cooling water circulates around the engine block and oil cooler, absorbing heat (approx. 90 °C).
- Exhaust Gas: The hot exhaust (often 400 °C+) passes through an exhaust gas heat exchanger.
This captured energy heats water or generates steam, providing process heat for industrial processes, hot water for district heating, or space heating.
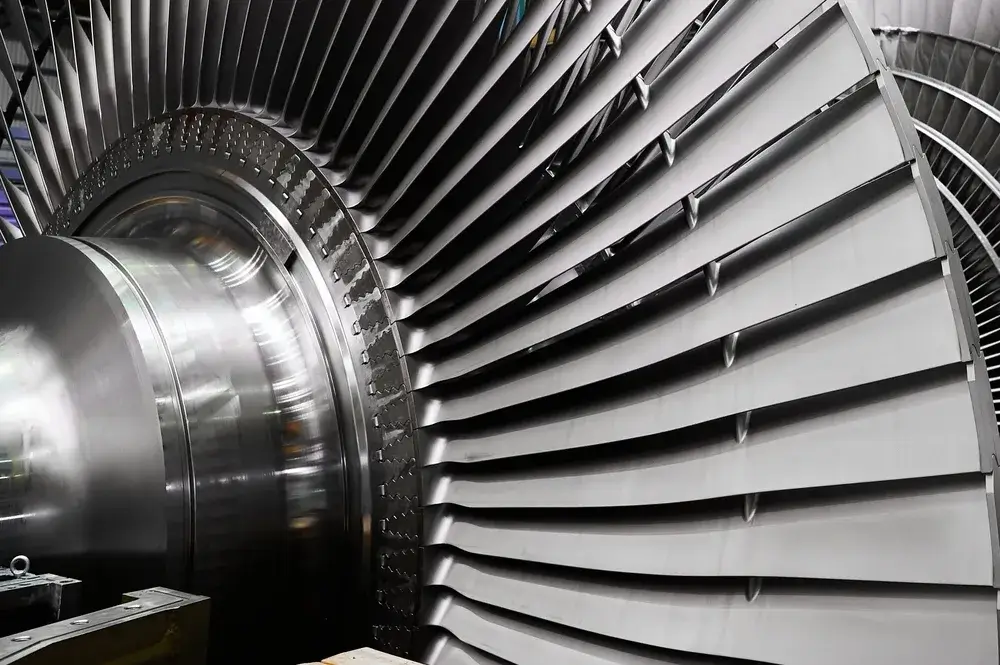
Technologies: Turbine vs. Engine
While the principle is the same, the hardware differs based on the CHP applications:
- Reciprocating Engine (Gas Engine): The standard for chp plants from 50 kW to 10 MW. They offer high efficiency, are flexible, and start quickly. This is the technology PowerUP specializes in.
- Gas Turbine: Used in very large industries requiring high-pressure steam.
- Steam Turbines: Often used with solid biomass or waste, where fuel is burned to create steam that drives the turbine.

Operational Strategies: Heat-led vs. Electricity-led
To maximize cost-effective operation, the control strategy is crucial.
In an Electricity-led mode, the unit runs to cover power generation needs or to feed into the grid when prices are high, with heat being a byproduct stored in a buffer tank. This is vital for energy security and microgrids to bridge power outages.
Conversely, in a Heat-led mode, common in greenhouses or residential complexes, the unit runs when thermal energy is required, with electricity generated as the byproduct.
Benefits for the Environment and Balance Sheet
The integration of CHP systems offers massive advantages over separate generation:
- Reduced Emissions: Using waste heat means burning less fuel overall, drastically cutting carbon emissions.
- Energy Security: On-site generation protects against grid instability.
- Financial Savings: Lower energy costs and potential revenue from grid services.
The Role of Fuel: From Fossil to Renewable
CHP installation is future-proof because the energy source can change. While many systems today run on natural gas, the transition to renewable energy is in full swing.
Modern engines are increasingly running on biogas, biomethane, or hydrogen. This transforms the CHP unit into a tool for the green energy transition.

How PowerUP Ensures Your CHP Works Efficiently
A combined heat and power plant is a high-performance athlete. It needs care to maintain high efficiency. Every drop in performance increases your energy bills.
We at PowerUP understand the technology down to the smallest bolt. We provide high-quality spare parts suitable for MWM and Jenbacher engines, perform condition-based overhauls to extend the life of your prime mover, and offer upgrades to modernize control systems for microgrids or new fuels. We ensure that the physics of cogeneration works for you, not against you.
















